Spaces:
Sleeping
A newer version of the Gradio SDK is available:
5.46.0
Dataset
Overview
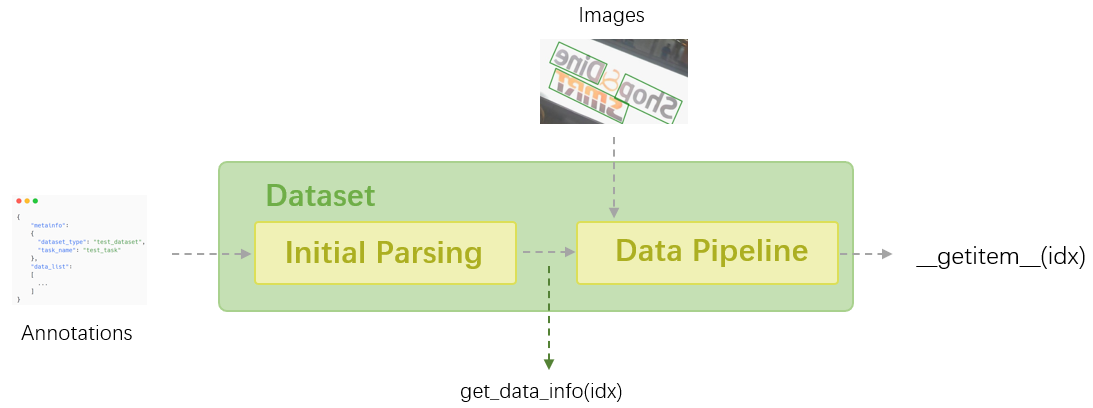
In MMOCR, all the datasets are processed via different Dataset classes based on mmengine.BaseDataset. Dataset classes are responsible for loading the data and performing initial parsing, then fed to data pipeline for data preprocessing, augmentation, formatting, etc.
In this tutorial, we will introduce some common interfaces of the Dataset class, and the usage of Dataset implementations in MMOCR as well as the annotation types they support.
Dataset class supports some advanced features, such as lazy initialization and data serialization, and takes advantage of various dataset wrappers to perform data concatenation, repeating, and category balancing. These content will not be covered in this tutorial, but you can read {external+mmengine:doc}`MMEngine: BaseDataset <advanced_tutorials/basedataset>` for more details.
Common Interfaces
Now, let's look at a concrete example and learn some typical interfaces of a Dataset class.
OCRDataset is a widely used Dataset implementation in MMOCR, and is suggested as a default Dataset type in MMOCR as its associated annotation format is flexible enough to support all the OCR tasks (more info). Now we will instantiate an OCRDataset object wherein the toy dataset in tests/data/det_toy_dataset will be loaded.
from mmocr.datasets import OCRDataset
from mmengine.registry import init_default_scope
init_default_scope('mmocr')
train_pipeline = [
dict(
type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(
type='LoadOCRAnnotations',
with_polygon=True,
with_bbox=True,
with_label=True,
),
dict(type='RandomCrop', min_side_ratio=0.1),
dict(type='Resize', scale=(640, 640), keep_ratio=True),
dict(type='Pad', size=(640, 640)),
dict(
type='PackTextDetInputs',
meta_keys=('img_path', 'ori_shape', 'img_shape'))
]
dataset = OCRDataset(
data_root='tests/data/det_toy_dataset',
ann_file='textdet_test.json',
test_mode=False,
pipeline=train_pipeline)
Let's peek the size of this dataset:
>>> print(len(dataset))
10
Typically, a Dataset class loads and stores two types of information: (1) meta information: Some meta descriptors of the dataset's property, such as available object categories in this dataset. (2) annotation: The path to images, and their labels. We can access the meta information in dataset.metainfo:
>>> from pprint import pprint
>>> pprint(dataset.metainfo)
{'category': [{'id': 0, 'name': 'text'}],
'dataset_type': 'TextDetDataset',
'task_name': 'textdet'}
As for the annotations, we can access them via dataset.get_data_info(idx), which returns a dictionary containing the information of the idx-th sample in the dataset that is initially parsed, but not yet processed by data pipeline.
>>> from pprint import pprint
>>> pprint(dataset.get_data_info(0))
{'height': 720,
'img_path': 'tests/data/det_toy_dataset/test/img_10.jpg',
'instances': [{'bbox': [260.0, 138.0, 284.0, 158.0],
'bbox_label': 0,
'ignore': True,
'polygon': [261, 138, 284, 140, 279, 158, 260, 158]},
...,
{'bbox': [1011.0, 157.0, 1079.0, 173.0],
'bbox_label': 0,
'ignore': True,
'polygon': [1011, 157, 1079, 160, 1076, 173, 1011, 170]}],
'sample_idx': 0,
'seg_map': 'test/gt_img_10.txt',
'width': 1280}
On the other hand, we can get the sample fully processed by data pipeline via dataset[idx] or dataset.__getitem__(idx), which is directly feedable to models and perform a full train/test cycle. It has two fields:
inputs: The image after data augmentation;data_samples: The DataSample that contains the augmented annotations, and meta information appended by some data transforms to keep track of some key properties of this sample.
>>> pprint(dataset[0])
{'data_samples': <TextDetDataSample(
META INFORMATION
ori_shape: (720, 1280)
img_path: 'tests/data/det_toy_dataset/imgs/test/img_10.jpg'
img_shape: (640, 640)
DATA FIELDS
gt_instances: <InstanceData(
META INFORMATION
DATA FIELDS
labels: tensor([0, 0, 0])
polygons: [array([207.33984 , 104.65409 , 208.34634 , 84.528305, 231.49594 ,
86.54088 , 226.46341 , 104.65409 , 207.33984 , 104.65409 ],
dtype=float32), array([237.53496 , 103.6478 , 235.52196 , 84.528305, 365.36096 ,
86.54088 , 364.35446 , 107.67296 , 237.53496 , 103.6478 ],
dtype=float32), array([105.68293, 166.03773, 105.68293, 151.94969, 177.14471, 150.94339,
178.15121, 165.03145, 105.68293, 166.03773], dtype=float32)]
ignored: tensor([ True, False, True])
bboxes: tensor([[207.3398, 84.5283, 231.4959, 104.6541],
[235.5220, 84.5283, 365.3610, 107.6730],
[105.6829, 150.9434, 178.1512, 166.0377]])
) at 0x7f7359f04fa0>
) at 0x7f735a0508e0>,
'inputs': tensor([[[129, 111, 131, ..., 0, 0, 0], ...
[ 19, 18, 15, ..., 0, 0, 0]]], dtype=torch.uint8)}
Dataset Classes and Annotation Formats
Each Dataset implementation can only load datasets in a specific annotation format. Here lists all supported Dataset classes and their compatible annotation formats, as well as an example config that showcases how to use them in practice.
If you are not familiar with the config system, you may find [Dataset Configuration](../user_guides/dataset_prepare.md#dataset-configuration) helpful.
OCRDataset
Usually, there are many different types of annotations in OCR datasets, and the formats often vary between different subtasks, such as text detection and text recognition. These differences can result in the need for different data loading code when using different datasets, increasing the learning and maintenance costs for users.
In MMOCR, we propose a unified dataset format that can adapt to all three subtasks of OCR: text detection, text recognition, and text spotting. This design maximizes the uniformity of the dataset, allows for the reuse of data annotations across different tasks, and makes dataset management more convenient. Considering that popular dataset formats are still inconsistent, MMOCR provides Dataset Preparer to help users convert their datasets to MMOCR format. We also strongly encourage researchers to develop their own datasets based on this data format.
Annotation Format
This annotation file is a .json file that stores a dict, containing both metainfo and data_list, where the former includes basic information about the dataset and the latter consists of the label item of each target instance. Here presents an extensive list of all the fields in the annotation file, but some fields are used in a subset of tasks and can be ignored in other tasks.
{
"metainfo":
{
"dataset_type": "TextDetDataset", # Options: TextDetDataset/TextRecogDataset/TextSpotterDataset
"task_name": "textdet", # Options: textdet/textspotter/textrecog
"category": [{"id": 0, "name": "text"}] # Used in textdet/textspotter
},
"data_list":
[
{
"img_path": "test_img.jpg",
"height": 604,
"width": 640,
"instances": # multiple instances in one image
[
{
"bbox": [0, 0, 10, 20], # in textdet/textspotter, [x1, y1, x2, y2].
"bbox_label": 0, # The object category, always 0 (text) in MMOCR
"polygon": [0, 0, 0, 10, 10, 20, 20, 0], # in textdet/textspotter. [x1, y1, x2, y2, ....]
"text": "mmocr", # in textspotter/textrecog
"ignore": False # in textspotter/textdet. Whether to ignore this sample during training
},
#...
],
}
#... multiple images
]
}
Example Config
Here is a part of config example where we make train_dataloader use OCRDataset to load the ICDAR2015 dataset for a text detection model. Keep in mind that OCRDataset can load any OCR datasets prepared by Dataset Preparer regardless of its task. That is, you can use it for text recognition and text spotting, but you still have to modify the transform types in pipeline according to the needs of different tasks.
pipeline = [
dict(
type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(
type='LoadOCRAnnotations',
with_polygon=True,
with_bbox=True,
with_label=True,
),
dict(
type='PackTextDetInputs',
meta_keys=('img_path', 'ori_shape', 'img_shape'))
]
icdar2015_textdet_train = dict(
type='OCRDataset',
data_root='data/icdar2015',
ann_file='textdet_train.json',
filter_cfg=dict(filter_empty_gt=True, min_size=32),
pipeline=pipeline)
train_dataloader = dict(
batch_size=16,
num_workers=8,
persistent_workers=True,
sampler=dict(type='DefaultSampler', shuffle=True),
dataset=icdar2015_textdet_train)
RecogLMDBDataset
Reading images or labels from files can be slow when data are excessive, e.g. on a scale of millions. Besides, in academia, most of the scene text recognition datasets are stored in lmdb format, including images and labels. (Example)
To get closer to the mainstream practice and enhance the data storage efficiency, MMOCR supports loading images and labels from lmdb datasets via RecogLMDBDataset.
Annotation Format
MMOCR requires the following keys for LMDB datasets:
num_samples: The parameter describing the data volume of the dataset.- The keys of images and labels are in the
format of
image-000000001andlabel-000000001, respectively. The index starts from 1.
MMOCR has a toy LMDB dataset in tests/data/rec_toy_dataset/imgs.lmdb.
You can get a sense of the format with the following code snippet.
>>> import lmdb
>>>
>>> env = lmdb.open('tests/data/rec_toy_dataset/imgs.lmdb')
>>> txn = env.begin()
>>> for k, v in txn.cursor():
>>> print(k, v)
b'image-000000001' b'\xff...'
b'image-000000002' b'\xff...'
b'image-000000003' b'\xff...'
b'image-000000004' b'\xff...'
b'image-000000005' b'\xff...'
b'image-000000006' b'\xff...'
b'image-000000007' b'\xff...'
b'image-000000008' b'\xff...'
b'image-000000009' b'\xff...'
b'image-000000010' b'\xff...'
b'label-000000001' b'GRAND'
b'label-000000002' b'HOTEL'
b'label-000000003' b'HOTEL'
b'label-000000004' b'PACIFIC'
b'label-000000005' b'03/09/2009'
b'label-000000006' b'ANING'
b'label-000000007' b'Virgin'
b'label-000000008' b'america'
b'label-000000009' b'ATTACK'
b'label-000000010' b'DAVIDSON'
b'num-samples' b'10'
Example Config
Here is a part of config example where we make train_dataloader use RecogLMDBDataset to load the toy dataset. Since RecogLMDBDataset loads images as numpy arrays, don't forget to use LoadImageFromNDArray instead of LoadImageFromFile in the pipeline for successful loading.
pipeline = [
dict(
type='LoadImageFromNDArray'),
dict(
type='LoadOCRAnnotations',
with_text=True,
),
dict(
type='PackTextRecogInputs',
meta_keys=('img_path', 'ori_shape', 'img_shape'))
]
toy_textrecog_train = dict(
type='RecogLMDBDataset',
data_root='tests/data/rec_toy_dataset/',
ann_file='imgs.lmdb',
pipeline=pipeline)
train_dataloader = dict(
batch_size=16,
num_workers=8,
persistent_workers=True,
sampler=dict(type='DefaultSampler', shuffle=True),
dataset=toy_textrecog_train)
RecogTextDataset
Prior to MMOCR 1.0, MMOCR 0.x takes text files as input for text recognition. These formats has been deprecated in MMOCR 1.0, and this class could be removed anytime in the future. More info
Annotation Format
Text files can either be in txt format or jsonl format. The simple .txt annotations separate image name and word annotation by a blank space, which cannot handle the case when spaces are included in a text instance.
img1.jpg OpenMMLab
img2.jpg MMOCR
The JSON Line format uses a dictionary-like structure to represent the annotations, where the keys filename and text store the image name and word label, respectively.
{"filename": "img1.jpg", "text": "OpenMMLab"}
{"filename": "img2.jpg", "text": "MMOCR"}
Example Config
Here is a part of config example where we use RecogTextDataset to load the old txt labels in training, and the old jsonl labels in testing.
pipeline = [
dict(
type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(
type='LoadOCRAnnotations',
with_polygon=True,
with_bbox=True,
with_label=True,
),
dict(
type='PackTextDetInputs',
meta_keys=('img_path', 'ori_shape', 'img_shape'))
]
# loading 0.x txt format annos
txt_dataset = dict(
type='RecogTextDataset',
data_root=data_root,
ann_file='old_label.txt',
data_prefix=dict(img_path='imgs'),
parser_cfg=dict(
type='LineStrParser',
keys=['filename', 'text'],
keys_idx=[0, 1]),
pipeline=pipeline)
train_dataloader = dict(
batch_size=16,
num_workers=8,
persistent_workers=True,
sampler=dict(type='DefaultSampler', shuffle=True),
dataset=txt_dataset)
# loading 0.x json line format annos
jsonl_dataset = dict(
type='RecogTextDataset',
data_root=data_root,
ann_file='old_label.jsonl',
data_prefix=dict(img_path='imgs'),
parser_cfg=dict(
type='LineJsonParser',
keys=['filename', 'text'],
pipeline=pipeline))
test_dataloader = dict(
batch_size=16,
num_workers=8,
persistent_workers=True,
sampler=dict(type='DefaultSampler', shuffle=False),
dataset=jsonl_dataset)
IcdarDataset
Prior to MMOCR 1.0, MMOCR 0.x takes COCO-like format annotations as input for text detection. These formats has been deprecated in MMOCR 1.0, and this class could be removed anytime in the future. More info
Annotation Format
{
"images": [
{
"id": 1,
"width": 800,
"height": 600,
"file_name": "test.jpg"
}
],
"annotations": [
{
"id": 1,
"image_id": 1,
"category_id": 1,
"bbox": [0,0,10,10],
"segmentation": [
[0,0,10,0,10,10,0,10]
],
"area": 100,
"iscrowd": 0
}
]
}
Example Config
Here is a part of config example where we make train_dataloader use IcdarDataset to load the old labels.
pipeline = [
dict(
type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(
type='LoadOCRAnnotations',
with_polygon=True,
with_bbox=True,
with_label=True,
),
dict(
type='PackTextDetInputs',
meta_keys=('img_path', 'ori_shape', 'img_shape'))
]
icdar2015_textdet_train = dict(
type='IcdarDatasetDataset',
data_root='data/det/icdar2015',
ann_file='instances_training.json',
filter_cfg=dict(filter_empty_gt=True, min_size=32),
pipeline=pipeline)
train_dataloader = dict(
batch_size=16,
num_workers=8,
persistent_workers=True,
sampler=dict(type='DefaultSampler', shuffle=True),
dataset=icdar2015_textdet_train)
WildReceiptDataset
It's customized for WildReceipt dataset only.
Annotation Format
// Close Set
{
"file_name": "image_files/Image_16/11/d5de7f2a20751e50b84c747c17a24cd98bed3554.jpeg",
"height": 1200,
"width": 1600,
"annotations":
[
{
"box": [550.0, 190.0, 937.0, 190.0, 937.0, 104.0, 550.0, 104.0],
"text": "SAFEWAY",
"label": 1
},
{
"box": [1048.0, 211.0, 1074.0, 211.0, 1074.0, 196.0, 1048.0, 196.0],
"text": "TM",
"label": 25
}
], //...
}
// Open Set
{
"file_name": "image_files/Image_12/10/845be0dd6f5b04866a2042abd28d558032ef2576.jpeg",
"height": 348,
"width": 348,
"annotations":
[
{
"box": [114.0, 19.0, 230.0, 19.0, 230.0, 1.0, 114.0, 1.0],
"text": "CHOEUN",
"label": 2,
"edge": 1
},
{
"box": [97.0, 35.0, 236.0, 35.0, 236.0, 19.0, 97.0, 19.0],
"text": "KOREANRESTAURANT",
"label": 2,
"edge": 1
}
]
}
Example Config
Please refer to SDMGR's config for more details.