Spaces:
Sleeping
Sleeping
File size: 17,138 Bytes
14c9181 |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 441 442 443 444 445 446 447 448 449 450 451 452 453 454 455 456 457 458 459 460 461 462 463 464 465 466 467 468 469 470 471 472 473 474 475 476 477 478 479 480 481 482 483 484 485 486 487 488 489 490 491 492 |
# Dataset
## Overview
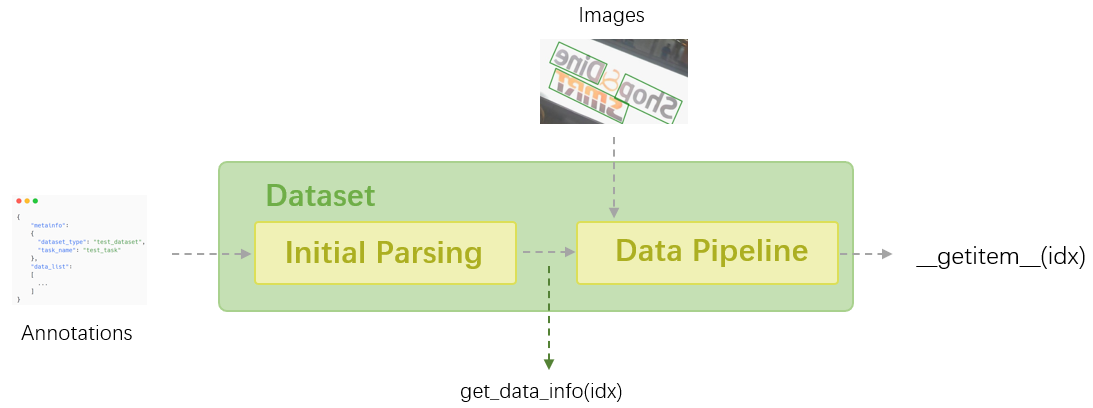
In MMOCR, all the datasets are processed via different Dataset classes based on [mmengine.BaseDataset](mmengine.dataset.BaseDataset). Dataset classes are responsible for loading the data and performing initial parsing, then fed to [data pipeline](./transforms.md) for data preprocessing, augmentation, formatting, etc.
<div align="center">
</div>
In this tutorial, we will introduce some common interfaces of the Dataset class, and the usage of Dataset implementations in MMOCR as well as the annotation types they support.
```{tip}
Dataset class supports some advanced features, such as lazy initialization and data serialization, and takes advantage of various dataset wrappers to perform data concatenation, repeating, and category balancing. These content will not be covered in this tutorial, but you can read {external+mmengine:doc}`MMEngine: BaseDataset <advanced_tutorials/basedataset>` for more details.
```
## Common Interfaces
Now, let's look at a concrete example and learn some typical interfaces of a Dataset class.
`OCRDataset` is a widely used Dataset implementation in MMOCR, and is suggested as a default Dataset type in MMOCR as its associated annotation format is flexible enough to support *all* the OCR tasks ([more info](#ocrdataset)). Now we will instantiate an `OCRDataset` object wherein the toy dataset in `tests/data/det_toy_dataset` will be loaded.
```python
from mmocr.datasets import OCRDataset
from mmengine.registry import init_default_scope
init_default_scope('mmocr')
train_pipeline = [
dict(
type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(
type='LoadOCRAnnotations',
with_polygon=True,
with_bbox=True,
with_label=True,
),
dict(type='RandomCrop', min_side_ratio=0.1),
dict(type='Resize', scale=(640, 640), keep_ratio=True),
dict(type='Pad', size=(640, 640)),
dict(
type='PackTextDetInputs',
meta_keys=('img_path', 'ori_shape', 'img_shape'))
]
dataset = OCRDataset(
data_root='tests/data/det_toy_dataset',
ann_file='textdet_test.json',
test_mode=False,
pipeline=train_pipeline)
```
Let's peek the size of this dataset:
```python
>>> print(len(dataset))
10
```
Typically, a Dataset class loads and stores two types of information: (1) **meta information**: Some meta descriptors of the dataset's property, such as available object categories in this dataset. (2) **annotation**: The path to images, and their labels. We can access the meta information in `dataset.metainfo`:
```python
>>> from pprint import pprint
>>> pprint(dataset.metainfo)
{'category': [{'id': 0, 'name': 'text'}],
'dataset_type': 'TextDetDataset',
'task_name': 'textdet'}
```
As for the annotations, we can access them via `dataset.get_data_info(idx)`, which returns a dictionary containing the information of the `idx`-th sample in the dataset that is initially parsed, but not yet processed by [data pipeline](./transforms.md).
```python
>>> from pprint import pprint
>>> pprint(dataset.get_data_info(0))
{'height': 720,
'img_path': 'tests/data/det_toy_dataset/test/img_10.jpg',
'instances': [{'bbox': [260.0, 138.0, 284.0, 158.0],
'bbox_label': 0,
'ignore': True,
'polygon': [261, 138, 284, 140, 279, 158, 260, 158]},
...,
{'bbox': [1011.0, 157.0, 1079.0, 173.0],
'bbox_label': 0,
'ignore': True,
'polygon': [1011, 157, 1079, 160, 1076, 173, 1011, 170]}],
'sample_idx': 0,
'seg_map': 'test/gt_img_10.txt',
'width': 1280}
```
On the other hand, we can get the sample fully processed by data pipeline via `dataset[idx]` or `dataset.__getitem__(idx)`, which is directly feedable to models and perform a full train/test cycle. It has two fields:
- `inputs`: The image after data augmentation;
- `data_samples`: The [DataSample](./structures.md) that contains the augmented annotations, and meta information appended by some data transforms to keep track of some key properties of this sample.
```python
>>> pprint(dataset[0])
{'data_samples': <TextDetDataSample(
META INFORMATION
ori_shape: (720, 1280)
img_path: 'tests/data/det_toy_dataset/imgs/test/img_10.jpg'
img_shape: (640, 640)
DATA FIELDS
gt_instances: <InstanceData(
META INFORMATION
DATA FIELDS
labels: tensor([0, 0, 0])
polygons: [array([207.33984 , 104.65409 , 208.34634 , 84.528305, 231.49594 ,
86.54088 , 226.46341 , 104.65409 , 207.33984 , 104.65409 ],
dtype=float32), array([237.53496 , 103.6478 , 235.52196 , 84.528305, 365.36096 ,
86.54088 , 364.35446 , 107.67296 , 237.53496 , 103.6478 ],
dtype=float32), array([105.68293, 166.03773, 105.68293, 151.94969, 177.14471, 150.94339,
178.15121, 165.03145, 105.68293, 166.03773], dtype=float32)]
ignored: tensor([ True, False, True])
bboxes: tensor([[207.3398, 84.5283, 231.4959, 104.6541],
[235.5220, 84.5283, 365.3610, 107.6730],
[105.6829, 150.9434, 178.1512, 166.0377]])
) at 0x7f7359f04fa0>
) at 0x7f735a0508e0>,
'inputs': tensor([[[129, 111, 131, ..., 0, 0, 0], ...
[ 19, 18, 15, ..., 0, 0, 0]]], dtype=torch.uint8)}
```
## Dataset Classes and Annotation Formats
Each Dataset implementation can only load datasets in a specific annotation format. Here lists all supported Dataset classes and their compatible annotation formats, as well as an example config that showcases how to use them in practice.
```{note}
If you are not familiar with the config system, you may find [Dataset Configuration](../user_guides/dataset_prepare.md#dataset-configuration) helpful.
```
### OCRDataset
Usually, there are many different types of annotations in OCR datasets, and the formats often vary between different subtasks, such as text detection and text recognition. These differences can result in the need for different data loading code when using different datasets, increasing the learning and maintenance costs for users.
In MMOCR, we propose a unified dataset format that can adapt to all three subtasks of OCR: text detection, text recognition, and text spotting. This design maximizes the uniformity of the dataset, allows for the reuse of data annotations across different tasks, and makes dataset management more convenient. Considering that popular dataset formats are still inconsistent, MMOCR provides [Dataset Preparer](../user_guides/data_prepare/dataset_preparer.md) to help users convert their datasets to MMOCR format. We also strongly encourage researchers to develop their own datasets based on this data format.
#### Annotation Format
This annotation file is a `.json` file that stores a `dict`, containing both `metainfo` and `data_list`, where the former includes basic information about the dataset and the latter consists of the label item of each target instance. Here presents an extensive list of all the fields in the annotation file, but some fields are used in a subset of tasks and can be ignored in other tasks.
```python
{
"metainfo":
{
"dataset_type": "TextDetDataset", # Options: TextDetDataset/TextRecogDataset/TextSpotterDataset
"task_name": "textdet", # Options: textdet/textspotter/textrecog
"category": [{"id": 0, "name": "text"}] # Used in textdet/textspotter
},
"data_list":
[
{
"img_path": "test_img.jpg",
"height": 604,
"width": 640,
"instances": # multiple instances in one image
[
{
"bbox": [0, 0, 10, 20], # in textdet/textspotter, [x1, y1, x2, y2].
"bbox_label": 0, # The object category, always 0 (text) in MMOCR
"polygon": [0, 0, 0, 10, 10, 20, 20, 0], # in textdet/textspotter. [x1, y1, x2, y2, ....]
"text": "mmocr", # in textspotter/textrecog
"ignore": False # in textspotter/textdet. Whether to ignore this sample during training
},
#...
],
}
#... multiple images
]
}
```
#### Example Config
Here is a part of config example where we make `train_dataloader` use `OCRDataset` to load the ICDAR2015 dataset for a text detection model. Keep in mind that `OCRDataset` can load any OCR datasets prepared by Dataset Preparer regardless of its task. That is, you can use it for text recognition and text spotting, but you still have to modify the transform types in `pipeline` according to the needs of different tasks.
```python
pipeline = [
dict(
type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(
type='LoadOCRAnnotations',
with_polygon=True,
with_bbox=True,
with_label=True,
),
dict(
type='PackTextDetInputs',
meta_keys=('img_path', 'ori_shape', 'img_shape'))
]
icdar2015_textdet_train = dict(
type='OCRDataset',
data_root='data/icdar2015',
ann_file='textdet_train.json',
filter_cfg=dict(filter_empty_gt=True, min_size=32),
pipeline=pipeline)
train_dataloader = dict(
batch_size=16,
num_workers=8,
persistent_workers=True,
sampler=dict(type='DefaultSampler', shuffle=True),
dataset=icdar2015_textdet_train)
```
### RecogLMDBDataset
Reading images or labels from files can be slow when data are excessive, e.g. on a scale of millions. Besides, in academia, most of the scene text recognition datasets are stored in lmdb format, including images and labels. ([Example](https://github.com/clovaai/deep-text-recognition-benchmark))
To get closer to the mainstream practice and enhance the data storage efficiency, MMOCR supports loading images and labels from lmdb datasets via `RecogLMDBDataset`.
#### Annotation Format
MMOCR requires the following keys for LMDB datasets:
- `num_samples`: The parameter describing the data volume of the dataset.
- The keys of images and labels are in the
format of `image-000000001` and `label-000000001`, respectively. The index starts from 1.
MMOCR has a toy LMDB dataset in `tests/data/rec_toy_dataset/imgs.lmdb`.
You can get a sense of the format with the following code snippet.
```python
>>> import lmdb
>>>
>>> env = lmdb.open('tests/data/rec_toy_dataset/imgs.lmdb')
>>> txn = env.begin()
>>> for k, v in txn.cursor():
>>> print(k, v)
b'image-000000001' b'\xff...'
b'image-000000002' b'\xff...'
b'image-000000003' b'\xff...'
b'image-000000004' b'\xff...'
b'image-000000005' b'\xff...'
b'image-000000006' b'\xff...'
b'image-000000007' b'\xff...'
b'image-000000008' b'\xff...'
b'image-000000009' b'\xff...'
b'image-000000010' b'\xff...'
b'label-000000001' b'GRAND'
b'label-000000002' b'HOTEL'
b'label-000000003' b'HOTEL'
b'label-000000004' b'PACIFIC'
b'label-000000005' b'03/09/2009'
b'label-000000006' b'ANING'
b'label-000000007' b'Virgin'
b'label-000000008' b'america'
b'label-000000009' b'ATTACK'
b'label-000000010' b'DAVIDSON'
b'num-samples' b'10'
```
#### Example Config
Here is a part of config example where we make `train_dataloader` use `RecogLMDBDataset` to load the toy dataset. Since `RecogLMDBDataset` loads images as numpy arrays, don't forget to use `LoadImageFromNDArray` instead of `LoadImageFromFile` in the pipeline for successful loading.
```python
pipeline = [
dict(
type='LoadImageFromNDArray'),
dict(
type='LoadOCRAnnotations',
with_text=True,
),
dict(
type='PackTextRecogInputs',
meta_keys=('img_path', 'ori_shape', 'img_shape'))
]
toy_textrecog_train = dict(
type='RecogLMDBDataset',
data_root='tests/data/rec_toy_dataset/',
ann_file='imgs.lmdb',
pipeline=pipeline)
train_dataloader = dict(
batch_size=16,
num_workers=8,
persistent_workers=True,
sampler=dict(type='DefaultSampler', shuffle=True),
dataset=toy_textrecog_train)
```
### RecogTextDataset
Prior to MMOCR 1.0, MMOCR 0.x takes text files as input for text recognition. These formats has been deprecated in MMOCR 1.0, and this class could be removed anytime in the future. [More info](../migration/dataset.md)
#### Annotation Format
Text files can either be in `txt` format or `jsonl` format. The simple `.txt` annotations separate image name and word annotation by a blank space, which cannot handle the case when spaces are included in a text instance.
```text
img1.jpg OpenMMLab
img2.jpg MMOCR
```
The JSON Line format uses a dictionary-like structure to represent the annotations, where the keys `filename` and `text` store the image name and word label, respectively.
```json
{"filename": "img1.jpg", "text": "OpenMMLab"}
{"filename": "img2.jpg", "text": "MMOCR"}
```
#### Example Config
Here is a part of config example where we use `RecogTextDataset` to load the old txt labels in training, and the old jsonl labels in testing.
```python
pipeline = [
dict(
type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(
type='LoadOCRAnnotations',
with_polygon=True,
with_bbox=True,
with_label=True,
),
dict(
type='PackTextDetInputs',
meta_keys=('img_path', 'ori_shape', 'img_shape'))
]
# loading 0.x txt format annos
txt_dataset = dict(
type='RecogTextDataset',
data_root=data_root,
ann_file='old_label.txt',
data_prefix=dict(img_path='imgs'),
parser_cfg=dict(
type='LineStrParser',
keys=['filename', 'text'],
keys_idx=[0, 1]),
pipeline=pipeline)
train_dataloader = dict(
batch_size=16,
num_workers=8,
persistent_workers=True,
sampler=dict(type='DefaultSampler', shuffle=True),
dataset=txt_dataset)
# loading 0.x json line format annos
jsonl_dataset = dict(
type='RecogTextDataset',
data_root=data_root,
ann_file='old_label.jsonl',
data_prefix=dict(img_path='imgs'),
parser_cfg=dict(
type='LineJsonParser',
keys=['filename', 'text'],
pipeline=pipeline))
test_dataloader = dict(
batch_size=16,
num_workers=8,
persistent_workers=True,
sampler=dict(type='DefaultSampler', shuffle=False),
dataset=jsonl_dataset)
```
### IcdarDataset
Prior to MMOCR 1.0, MMOCR 0.x takes COCO-like format annotations as input for text detection. These formats has been deprecated in MMOCR 1.0, and this class could be removed anytime in the future. [More info](../migration/dataset.md)
#### Annotation Format
```json
{
"images": [
{
"id": 1,
"width": 800,
"height": 600,
"file_name": "test.jpg"
}
],
"annotations": [
{
"id": 1,
"image_id": 1,
"category_id": 1,
"bbox": [0,0,10,10],
"segmentation": [
[0,0,10,0,10,10,0,10]
],
"area": 100,
"iscrowd": 0
}
]
}
```
#### Example Config
Here is a part of config example where we make `train_dataloader` use `IcdarDataset` to load the old labels.
```python
pipeline = [
dict(
type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(
type='LoadOCRAnnotations',
with_polygon=True,
with_bbox=True,
with_label=True,
),
dict(
type='PackTextDetInputs',
meta_keys=('img_path', 'ori_shape', 'img_shape'))
]
icdar2015_textdet_train = dict(
type='IcdarDatasetDataset',
data_root='data/det/icdar2015',
ann_file='instances_training.json',
filter_cfg=dict(filter_empty_gt=True, min_size=32),
pipeline=pipeline)
train_dataloader = dict(
batch_size=16,
num_workers=8,
persistent_workers=True,
sampler=dict(type='DefaultSampler', shuffle=True),
dataset=icdar2015_textdet_train)
```
### WildReceiptDataset
It's customized for [WildReceipt](https://mmocr.readthedocs.io/en/dev-1.x/user_guides/data_prepare/datasetzoo.html#wildreceipt) dataset only.
#### Annotation Format
```json
// Close Set
{
"file_name": "image_files/Image_16/11/d5de7f2a20751e50b84c747c17a24cd98bed3554.jpeg",
"height": 1200,
"width": 1600,
"annotations":
[
{
"box": [550.0, 190.0, 937.0, 190.0, 937.0, 104.0, 550.0, 104.0],
"text": "SAFEWAY",
"label": 1
},
{
"box": [1048.0, 211.0, 1074.0, 211.0, 1074.0, 196.0, 1048.0, 196.0],
"text": "TM",
"label": 25
}
], //...
}
// Open Set
{
"file_name": "image_files/Image_12/10/845be0dd6f5b04866a2042abd28d558032ef2576.jpeg",
"height": 348,
"width": 348,
"annotations":
[
{
"box": [114.0, 19.0, 230.0, 19.0, 230.0, 1.0, 114.0, 1.0],
"text": "CHOEUN",
"label": 2,
"edge": 1
},
{
"box": [97.0, 35.0, 236.0, 35.0, 236.0, 19.0, 97.0, 19.0],
"text": "KOREANRESTAURANT",
"label": 2,
"edge": 1
}
]
}
```
#### Example Config
Please refer to [SDMGR's config](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmocr/blob/f30c16ce96bd2393570c04eeb9cf48a7916315cc/configs/kie/sdmgr/sdmgr_novisual_60e_wildreceipt.py) for more details.
|