# Fast-Inference with Ctranslate2
Speedup inference while reducing memory by 2x-4x using int8 inference in C++ on CPU or GPU.
quantized version of WizardLM/WizardCoder-15B-V1.0
pip install hf-hub-ctranslate2>=2.0.8 ctranslate2>=3.16.0
Converted on 2023-06-15 using
ct2-transformers-converter --model WizardLM/WizardCoder-15B-V1.0 --output_dir /home/michael/tmp-ct2fast-WizardCoder-15B-V1.0 --force --copy_files merges.txt tokenizer.json README.md tokenizer_config.json vocab.json generation_config.json special_tokens_map.json added_tokens.json .gitattributes --quantization int8_float16 --trust_remote_code
Checkpoint compatible to ctranslate2>=3.16.0 and hf-hub-ctranslate2>=2.0.8
compute_type=int8_float16fordevice="cuda"compute_type=int8fordevice="cpu"
from hf_hub_ctranslate2 import TranslatorCT2fromHfHub, GeneratorCT2fromHfHub
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
model_name = "michaelfeil/ct2fast-WizardCoder-15B-V1.0"
# use either TranslatorCT2fromHfHub or GeneratorCT2fromHfHub here, depending on model.
model = GeneratorCT2fromHfHub(
# load in int8 on CUDA
model_name_or_path=model_name,
device="cuda",
compute_type="int8_float16",
# tokenizer=AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("WizardLM/WizardCoder-15B-V1.0")
)
outputs = model.generate(
text=["def fibonnaci(", "User: How are you doing? Bot:"],
max_length=64,
include_prompt_in_result=False
)
print(outputs)
Licence and other remarks:
This is just a quantized version. Licence conditions are intended to be idential to original huggingface repo.
Original description
This is the Full-Weight of WizardCoder.
Repository: https://github.com/nlpxucan/WizardLM/tree/main/WizardCoder
Twitter: https://twitter.com/WizardLM_AI/status/1669109414559911937
Paper: Is coming, with brand-new Evol+ methods for code LLMs.
Demos (Only support code-related English instructions now.):
Demo, Backup Demo1, Backup Demo2, Backup Demo3
WizardCoder: Empowering Code Large Language Models with Evol-Instruct
To develop our WizardCoder model, we begin by adapting the Evol-Instruct method specifically for coding tasks. This involves tailoring the prompt to the domain of code-related instructions. Subsequently, we fine-tune the Code LLM, StarCoder, utilizing the newly created instruction-following training set.
News
- 🔥 Our WizardCoder-15B-v1.0 model achieves the 57.3 pass@1 on the HumanEval Benchmarks, which is 22.3 points higher than the SOTA open-source Code LLMs.
- 🔥 We released WizardCoder-15B-v1.0 trained with 78k evolved code instructions. Please checkout the Model Weights, and Paper.
- 📣 Please refer to our Twitter account https://twitter.com/WizardLM_AI and HuggingFace Repo https://huggingface.co/WizardLM . We will use them to announce any new release at the 1st time.
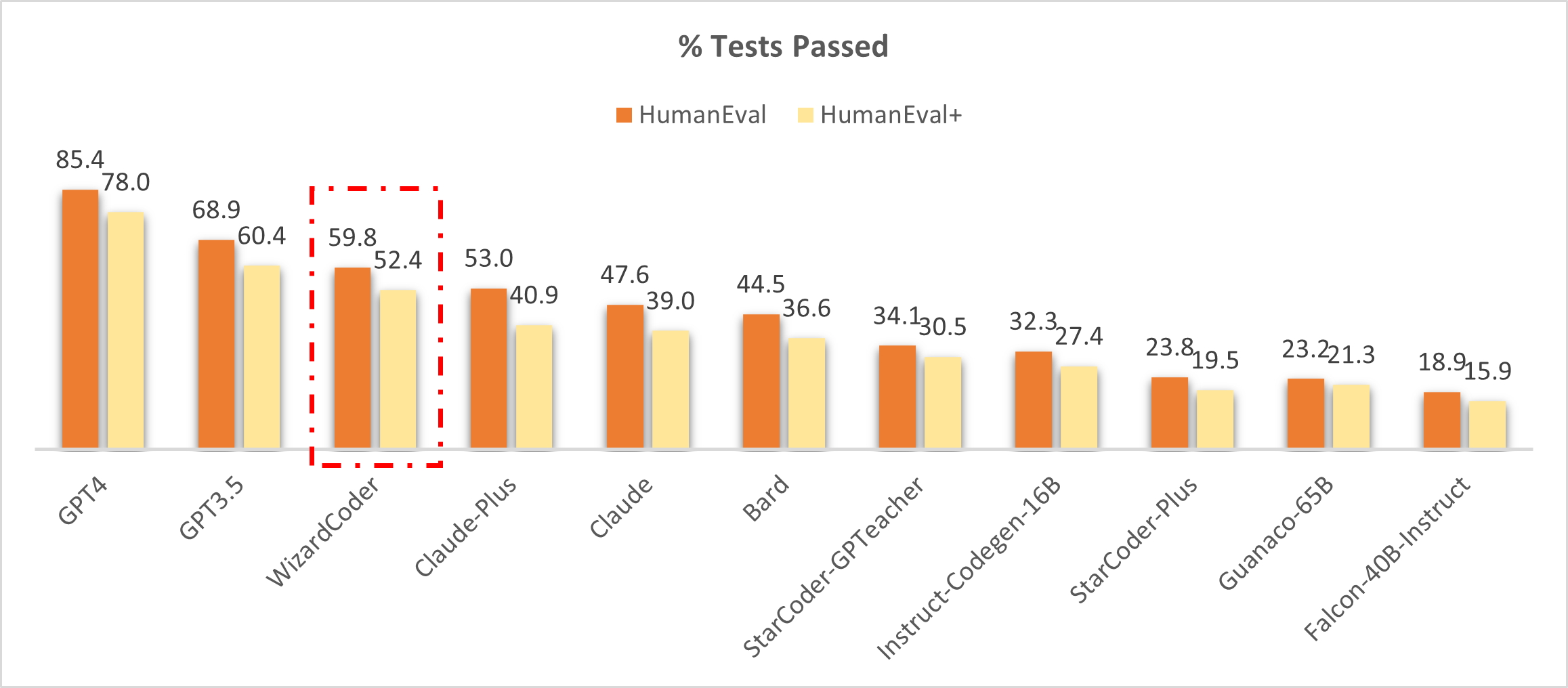
Comparing WizardCoder with the Closed-Source Models.
🔥 The following figure shows that our WizardCoder attains the third position in this benchmark, surpassing Claude-Plus (59.8 vs. 53.0) and Bard (59.8 vs. 44.5). Notably, our model exhibits a substantially smaller size compared to these models.
❗Note: In this study, we copy the scores for HumanEval and HumanEval+ from the LLM-Humaneval-Benchmarks. Notably, all the mentioned models generate code solutions for each problem utilizing a single attempt, and the resulting pass rate percentage is reported. Our WizardCoder generates answers using greedy decoding and tests with the same code.
Comparing WizardCoder with the Open-Source Models.
The following table clearly demonstrates that our WizardCoder exhibits a substantial performance advantage over all the open-source models. ❗If you are confused with the different scores of our model (57.3 and 59.8), please check the Notes.
| Model | HumanEval Pass@1 | MBPP Pass@1 |
|---|---|---|
| CodeGen-16B-Multi | 18.3 | 20.9 |
| CodeGeeX | 22.9 | 24.4 |
| LLaMA-33B | 21.7 | 30.2 |
| LLaMA-65B | 23.7 | 37.7 |
| PaLM-540B | 26.2 | 36.8 |
| PaLM-Coder-540B | 36.0 | 47.0 |
| PaLM 2-S | 37.6 | 50.0 |
| CodeGen-16B-Mono | 29.3 | 35.3 |
| Code-Cushman-001 | 33.5 | 45.9 |
| StarCoder-15B | 33.6 | 43.6* |
| InstructCodeT5+ | 35.0 | -- |
| WizardLM-30B 1.0 | 37.8 | -- |
| WizardCoder-15B 1.0 | 57.3 | 51.8 |
❗Note: The reproduced result of StarCoder on MBPP.
❗Note: The above table conducts a comprehensive comparison of our WizardCoder with other models on the HumanEval and MBPP benchmarks. We adhere to the approach outlined in previous studies by generating 20 samples for each problem to estimate the pass@1 score and evaluate with the same code. The scores of GPT4 and GPT3.5 reported by OpenAI are 67.0 and 48.1 (maybe these are the early version GPT4&3.5).
Call for Feedbacks
We welcome everyone to use your professional and difficult instructions to evaluate WizardCoder, and show us examples of poor performance and your suggestions in the issue discussion area. We are focusing on improving the Evol-Instruct now and hope to relieve existing weaknesses and issues in the the next version of WizardCoder. After that, we will open the code and pipeline of up-to-date Evol-Instruct algorithm and work with you together to improve it.
Contents
Online Demo
We will provide our latest models for you to try for as long as possible. If you find a link is not working, please try another one. At the same time, please try as many real-world and challenging code-related problems that you encounter in your work and life as possible. We will continue to evolve our models with your feedbacks.
Fine-tuning
We fine-tune WizardCoder using the modified code train.py from Llama-X.
We fine-tune StarCoder-15B with the following hyperparameters:
| Hyperparameter | StarCoder-15B |
|---|---|
| Batch size | 512 |
| Learning rate | 2e-5 |
| Epochs | 3 |
| Max length | 2048 |
| Warmup step | 30 |
| LR scheduler | cosine |
To reproduce our fine-tuning of WizardCoder, please follow the following steps:
- According to the instructions of Llama-X, install the environment, download the training code, and deploy. (Note:
deepspeed==0.9.2andtransformers==4.29.2) - Replace the
train.pywith thetrain_wizardcoder.pyin our repo (src/train_wizardcoder.py) - Login Huggingface:
huggingface-cli login
- Execute the following training command:
deepspeed train_wizardcoder.py \
--model_name_or_path "bigcode/starcoder" \
--data_path "/your/path/to/code_instruction_data.json" \
--output_dir "/your/path/to/ckpt" \
--num_train_epochs 3 \
--model_max_length 2048 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 16 \
--per_device_eval_batch_size 1 \
--gradient_accumulation_steps 4 \
--evaluation_strategy "no" \
--save_strategy "steps" \
--save_steps 50 \
--save_total_limit 2 \
--learning_rate 2e-5 \
--warmup_steps 30 \
--logging_steps 2 \
--lr_scheduler_type "cosine" \
--report_to "tensorboard" \
--gradient_checkpointing True \
--deepspeed configs/deepspeed_config.json \
--fp16 True
Inference
We provide the decoding script for WizardCoder, which reads a input file and generates corresponding responses for each sample, and finally consolidates them into an output file.
You can specify base_model, input_data_path and output_data_path in src\inference_wizardcoder.py to set the decoding model, path of input file and path of output file.
pip install jsonlines
The decoding command is:
python src\inference_wizardcoder.py \
--base_model "/your/path/to/ckpt" \
--input_data_path "/your/path/to/input/data.jsonl" \
--output_data_path "/your/path/to/output/result.jsonl"
The format of data.jsonl should be:
{"idx": 11, "Instruction": "Write a Python code to count 1 to 10."}
{"idx": 12, "Instruction": "Write a Jave code to sum 1 to 10."}
The prompt for our WizardCoder in src\inference_wizardcoder.py is:
Below is an instruction that describes a task. Write a response that appropriately completes the request.
### Instruction:
{instruction}
### Response:
Evaluation
We provide the evaluation script on HumanEval for WizardCoder.
- According to the instructions of HumanEval, install the environment.
- Run the following script to generate the answer.
model="/path/to/your/model"
temp=0.2
max_len=2048
pred_num=200
num_seqs_per_iter=2
output_path=preds/T${temp}_N${pred_num}
mkdir -p ${output_path}
echo 'Output path: '$output_path
echo 'Model to eval: '$model
# 164 problems, 21 per GPU if GPU=8
index=0
gpu_num=8
for ((i = 0; i < $gpu_num; i++)); do
start_index=$((i * 21))
end_index=$(((i + 1) * 21))
gpu=$((i))
echo 'Running process #' ${i} 'from' $start_index 'to' $end_index 'on GPU' ${gpu}
((index++))
(
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=$gpu python humaneval_gen.py --model ${model} \
--start_index ${start_index} --end_index ${end_index} --temperature ${temp} \
--num_seqs_per_iter ${num_seqs_per_iter} --N ${pred_num} --max_len ${max_len} --output_path ${output_path}
) &
if (($index % $gpu_num == 0)); then wait; fi
done
- Run the post processing code
src/process_humaneval.pyto collect the code completions from all answer files.
output_path=preds/T${temp}_N${pred_num}
echo 'Output path: '$output_path
python process_humaneval.py --path ${output_path} --out_path ${output_path}.jsonl --add_prompt
evaluate_functional_correctness ${output_path}.jsonl
Citation
Please cite the repo if you use the data or code in this repo.
@misc{luo2023wizardcoder,
title={WizardCoder: Empowering Code Large Language Models with Evol-Instruct},
author={Ziyang Luo and Can Xu and Pu Zhao and Qingfeng Sun and Xiubo Geng and Wenxiang Hu and Chongyang Tao and Jing Ma and Qingwei Lin and Daxin Jiang},
year={2023},
}
Disclaimer
The resources, including code, data, and model weights, associated with this project are restricted for academic research purposes only and cannot be used for commercial purposes. The content produced by any version of WizardCoder is influenced by uncontrollable variables such as randomness, and therefore, the accuracy of the output cannot be guaranteed by this project. This project does not accept any legal liability for the content of the model output, nor does it assume responsibility for any losses incurred due to the use of associated resources and output results.
- Downloads last month
- 4