datasets:
- BatsResearch/ctga-v1
language:
- en
library_name: transformers
pipeline_tag: text2text-generation
tags:
- data generation
license: apache-2.0
Bonito-v1 AWQ
You can find the original model at BatsResearch/bonito-v1
Variations
- GEMM: model.safetensors
- GEMV: model_gemv.safetensors
Model Card for bonito
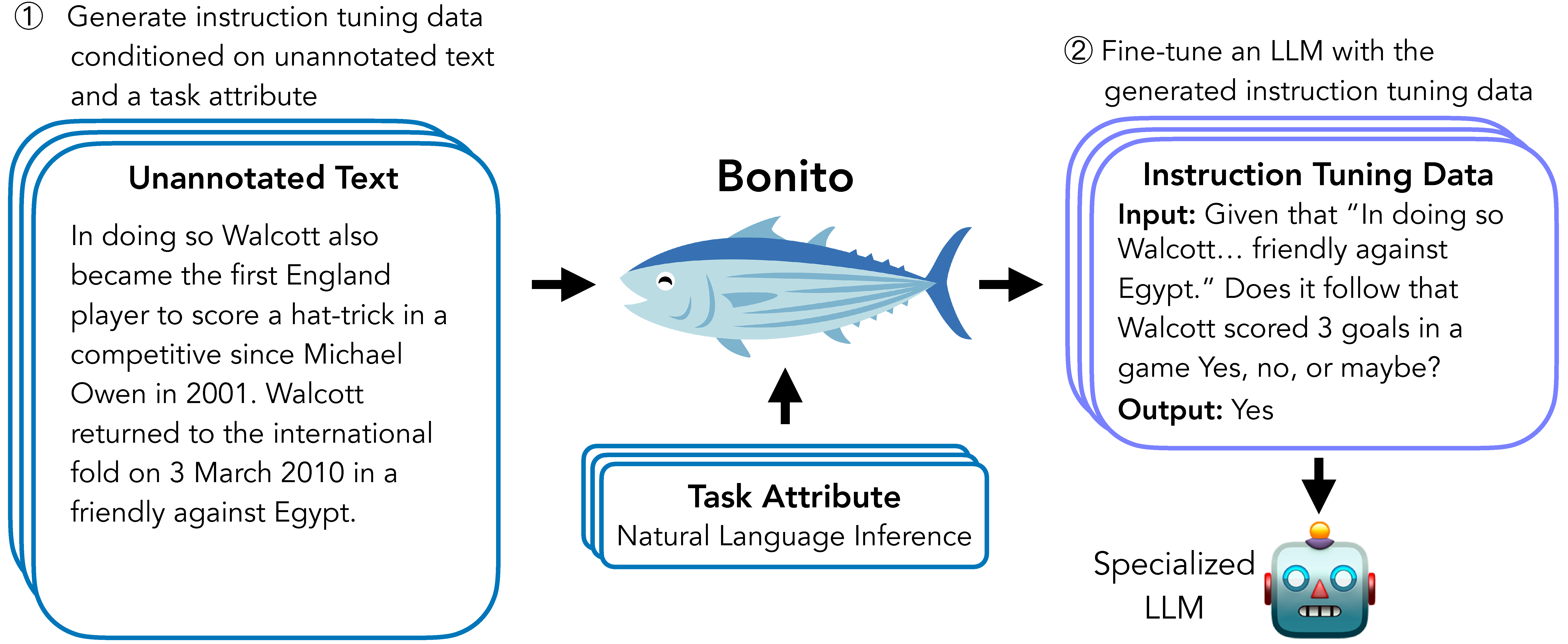
Bonito is an open-source model for conditional task generation: the task of converting unannotated text into task-specific training datasets for instruction tuning.
Model Details
Model Description
Bonito can be used to create synthetic instruction tuning datasets to adapt large language models on users' specialized, private data. In our paper, we show that Bonito can be used to adapt both pretrained and instruction tuned models to tasks without any annotations.
- Developed by: Nihal V. Nayak, Yiyang Nan, Avi Trost, and Stephen H. Bach
- Model type: MistralForCausalLM
- Language(s) (NLP): English
- License: TBD
- Finetuned from model:
mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1
Model Sources
- Repository: https://github.com/BatsResearch/bonito
- Paper: Arxiv link
Uses
Direct Use
To easily generate synthetic instruction tuning datasets, we recommend using the bonito package built using the transformers and the vllm libraries.
from bonito import Bonito, SamplingParams
from datasets import load_dataset
# Initialize the Bonito model
bonito = Bonito()
# load dataaset with unannotated text
unannotated_text = load_dataset(
"BatsResearch/bonito-experiment",
"unannotated_contract_nli"
)["train"].select(range(10))
# Generate synthetic instruction tuning dataset
sampling_params = SamplingParams(max_tokens=256, top_p=0.95, temperature=0.5, n=1)
synthetic_dataset = bonito.generate_tasks(
unannotated_text,
context_col="input",
task_type="nli",
sampling_params=sampling_params
)
Out-of-Scope Use
Our model is trained to generate the following task types: summarization, sentiment analysis, multiple-choice question answering, extractive question answering, topic classification, natural language inference, question generation, text generation, question answering without choices, paraphrase identification, sentence completion, yes-no question answering, word sense disambiguation, paraphrase generation, textual entailment, and coreference resolution. The model might not produce accurate synthetic tasks beyond these task types.