# Useful Tools
## Visualization Tools
### Dataset Visualization Tool
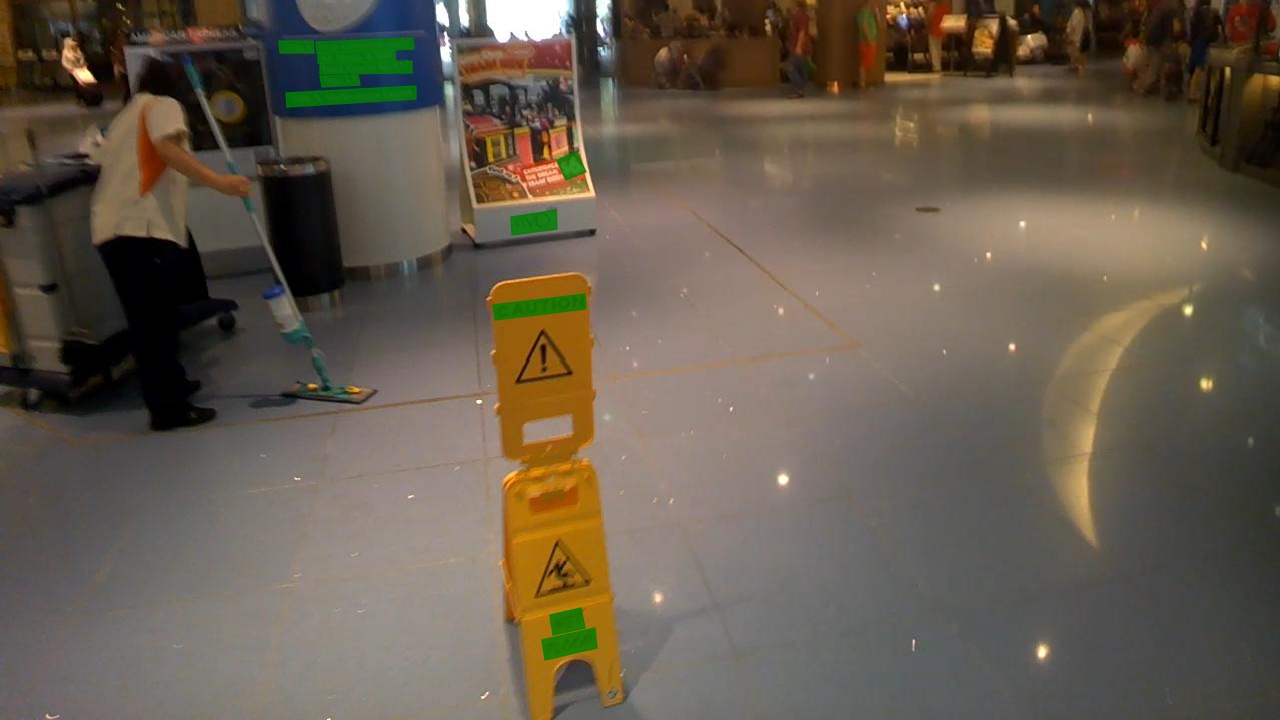
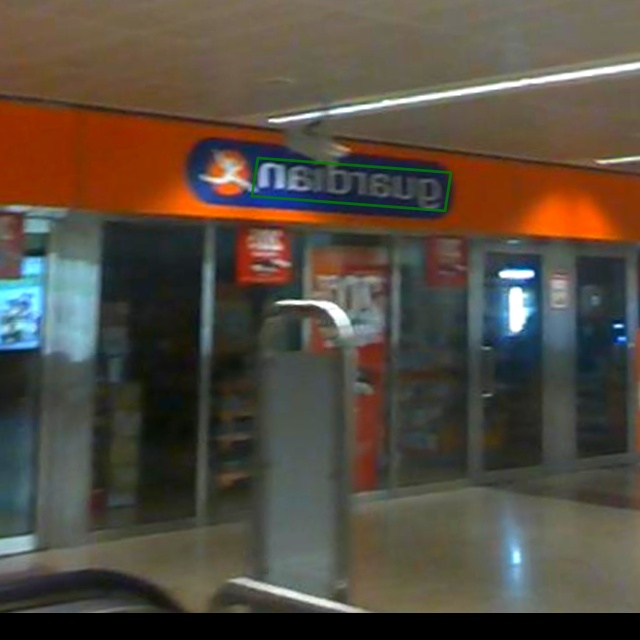
MMOCR provides a dataset visualization tool `tools/visualizations/browse_datasets.py` to help users troubleshoot possible dataset-related problems. You just need to specify the path to the training config (usually stored in `configs/textdet/dbnet/xxx.py`) or the dataset config (usually stored in `configs/textdet/_base_/datasets/xxx.py`), and the tool will automatically plots the transformed (or original) images and labels.
#### Usage
```bash
python tools/visualizations/browse_dataset.py \
${CONFIG_FILE} \
[-o, --output-dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}] \
[-p, --phase ${DATASET_PHASE}] \
[-m, --mode ${DISPLAY_MODE}] \
[-t, --task ${DATASET_TASK}] \
[-n, --show-number ${NUMBER_IMAGES_DISPLAY}] \
[-i, --show-interval ${SHOW_INTERRVAL}] \
[--cfg-options ${CFG_OPTIONS}]
```
| ARGS | Type | Description |
| ------------------- | ------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
| config | str | (required) Path to the config. |
| -o, --output-dir | str | If GUI is not available, specifying an output path to save the visualization results. |
| -p, --phase | str | Phase of dataset to visualize. Use "train", "test" or "val" if you just want to visualize the default split. It's also possible to be a dataset variable name, which might be useful when a dataset split has multiple variants in the config. |
| -m, --mode | `original`, `transformed`, `pipeline` | Display mode: display original pictures or transformed pictures or comparison pictures.`original` only visualizes the original dataset & annotations; `transformed` shows the resulting images processed through all the transforms; `pipeline` shows all the intermediate images. Defaults to "transformed". |
| -t, --task | `auto`, `textdet`, `textrecog` | Specify the task type of the dataset. If `auto`, the task type will be inferred from the config. If the script is unable to infer the task type, you need to specify it manually. Defaults to `auto`. |
| -n, --show-number | int | The number of samples to visualized. If not specified, display all images in the dataset. |
| -i, --show-interval | float | Interval of visualization (s), defaults to 2. |
| --cfg-options | float | Override configs.[Example](./config.md#command-line-modification) |
#### Examples
The following example demonstrates how to use the tool to visualize the training data used by the "DBNet_R50_icdar2015" model.
```Bash
# Example: Visualizing the training data used by dbnet_r50dcn_v2_fpnc_1200e_icadr2015 model
python tools/visualizations/browse_dataset.py configs/textdet/dbnet/dbnet_resnet50-dcnv2_fpnc_1200e_icdar2015.py
```
By default, the visualization mode is "transformed", and you will see the images & annotations being transformed by the pipeline:


 If you just want to visualize the original dataset, simply set the mode to "original":
```Bash
python tools/visualizations/browse_dataset.py configs/textdet/dbnet/dbnet_resnet50-dcnv2_fpnc_1200e_icdar2015.py -m original
```
Or, to visualize the entire pipeline:
```Bash
python tools/visualizations/browse_dataset.py configs/textdet/dbnet/dbnet_resnet50-dcnv2_fpnc_1200e_icdar2015.py -m pipeline
```
In addition, users can also visualize the original images and their corresponding labels of the dataset by specifying the path to the dataset config file, for example:
```Bash
python tools/visualizations/browse_dataset.py configs/textrecog/_base_/datasets/icdar2015.py
```
Some datasets might have multiple variants. For example, the test split of `icdar2015` textrecog dataset has two variants, which the [base dataset config](/configs/textrecog/_base_/datasets/icdar2015.py) defines as follows:
```python
icdar2015_textrecog_test = dict(
ann_file='textrecog_test.json',
# ...
)
icdar2015_1811_textrecog_test = dict(
ann_file='textrecog_test_1811.json',
# ...
)
```
In this case, you can specify the variant name to visualize the corresponding dataset:
```Bash
python tools/visualizations/browse_dataset.py configs/textrecog/_base_/datasets/icdar2015.py -p icdar2015_1811_textrecog_test
```
Based on this tool, users can easily verify if the annotation of a custom dataset is correct.
### Hyper-parameter Scheduler Visualization
This tool aims to help the user to check the hyper-parameter scheduler of the optimizer (without training), which support the "learning rate" or "momentum"
#### Introduce the scheduler visualization tool
```bash
python tools/visualizations/vis_scheduler.py \
${CONFIG_FILE} \
[-p, --parameter ${PARAMETER_NAME}] \
[-d, --dataset-size ${DATASET_SIZE}] \
[-n, --ngpus ${NUM_GPUs}] \
[-s, --save-path ${SAVE_PATH}] \
[--title ${TITLE}] \
[--style ${STYLE}] \
[--window-size ${WINDOW_SIZE}] \
[--cfg-options]
```
**Description of all arguments**:
- `config`: The path of a model config file.
- **`-p, --parameter`**: The param to visualize its change curve, choose from "lr" and "momentum". Default to use "lr".
- **`-d, --dataset-size`**: The size of the datasets. If set,`build_dataset` will be skipped and `${DATASET_SIZE}` will be used as the size. Default to use the function `build_dataset`.
- **`-n, --ngpus`**: The number of GPUs used in training, default to be 1.
- **`-s, --save-path`**: The learning rate curve plot save path, default not to save.
- `--title`: Title of figure. If not set, default to be config file name.
- `--style`: Style of plt. If not set, default to be `whitegrid`.
- `--window-size`: The shape of the display window. If not specified, it will be set to `12*7`. If used, it must be in the format `'W*H'`.
- `--cfg-options`: Modifications to the configuration file, refer to [Learn about Configs](../user_guides/config.md).
```{note}
Loading annotations maybe consume much time, you can directly specify the size of the dataset with `-d, dataset-size` to save time.
```
#### How to plot the learning rate curve without training
You can use the following command to plot the step learning rate schedule used in the config `configs/textdet/dbnet/dbnet_resnet50-dcnv2_fpnc_1200e_icdar2015.py`:
```bash
python tools/visualizations/vis_scheduler.py configs/textdet/dbnet/dbnet_resnet50-dcnv2_fpnc_1200e_icdar2015.py -d 100
```
## Analysis Tools
### Offline Evaluation Tool
For saved prediction results, we provide an offline evaluation script `tools/analysis_tools/offline_eval.py`. The following example demonstrates how to use this tool to evaluate the output of the "PSENet" model offline.
```Bash
# When running the test script for the first time, you can save the output of the model by specifying the --save-preds parameter
python tools/test.py ${CONFIG_FILE} ${CHECKPOINT_FILE} --save-preds
# Example: Testing on PSENet
python tools/test.py configs/textdet/psenet/psenet_r50_fpnf_600e_icdar2015.py epoch_600.pth --save-preds
# Then, using the saved outputs for offline evaluation
python tools/analysis_tool/offline_eval.py ${CONFIG_FILE} ${PRED_FILE}
# Example: Offline evaluation of saved PSENet results
python tools/analysis_tools/offline_eval.py configs/textdet/psenet/psenet_r50_fpnf_600e_icdar2015.py work_dirs/psenet_r50_fpnf_600e_icdar2015/epoch_600.pth_predictions.pkl
```
`-save-preds` saves the output to `work_dir/CONFIG_NAME/MODEL_NAME_predictions.pkl` by default
In addition, based on this tool, users can also convert predictions obtained from other libraries into MMOCR-supported formats, then use MMOCR's built-in metrics to evaluate them.
| ARGS | Type | Description |
| ------------- | ----- | ----------------------------------------------------------------- |
| config | str | (required) Path to the config. |
| pkl_results | str | (required) The saved predictions. |
| --cfg-options | float | Override configs.[Example](./config.md#command-line-modification) |
### Calculate FLOPs and the Number of Parameters
We provide a method to calculate the FLOPs and the number of parameters, first we install the dependencies using the following command.
```shell
pip install fvcore
```
The usage of the script to calculate FLOPs and the number of parameters is as follows.
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/get_flops.py ${config} --shape ${IMAGE_SHAPE}
```
| ARGS | Type | Description |
| ------- | ---- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| config | str | (required) Path to the config. |
| --shape | int | Image size to use when calculating FLOPs, such as `--shape 320 320`. Default is `640 640` |
For example, you can run the following command to get FLOPs and the number of parameters of `dbnet_resnet18_fpnc_100k_synthtext.py`:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/get_flops.py configs/textdet/dbnet/dbnet_resnet18_fpnc_100k_synthtext.py --shape 1024 1024
```
The output is as follows:
```shell
input shape is (1, 3, 1024, 1024)
| module | #parameters or shape | #flops |
| :------------------------ | :------------------- | :------ |
| model | 12.341M | 63.955G |
| backbone | 11.177M | 38.159G |
| backbone.conv1 | 9.408K | 2.466G |
| backbone.conv1.weight | (64, 3, 7, 7) | |
| backbone.bn1 | 0.128K | 83.886M |
| backbone.bn1.weight | (64,) | |
| backbone.bn1.bias | (64,) | |
| backbone.layer1 | 0.148M | 9.748G |
| backbone.layer1.0 | 73.984K | 4.874G |
| backbone.layer1.1 | 73.984K | 4.874G |
| backbone.layer2 | 0.526M | 8.642G |
| backbone.layer2.0 | 0.23M | 3.79G |
| backbone.layer2.1 | 0.295M | 4.853G |
| backbone.layer3 | 2.1M | 8.616G |
| backbone.layer3.0 | 0.919M | 3.774G |
| backbone.layer3.1 | 1.181M | 4.842G |
| backbone.layer4 | 8.394M | 8.603G |
| backbone.layer4.0 | 3.673M | 3.766G |
| backbone.layer4.1 | 4.721M | 4.837G |
| neck | 0.836M | 14.887G |
| neck.lateral_convs | 0.246M | 2.013G |
| neck.lateral_convs.0.conv | 16.384K | 1.074G |
| neck.lateral_convs.1.conv | 32.768K | 0.537G |
| neck.lateral_convs.2.conv | 65.536K | 0.268G |
| neck.lateral_convs.3.conv | 0.131M | 0.134G |
| neck.smooth_convs | 0.59M | 12.835G |
| neck.smooth_convs.0.conv | 0.147M | 9.664G |
| neck.smooth_convs.1.conv | 0.147M | 2.416G |
| neck.smooth_convs.2.conv | 0.147M | 0.604G |
| neck.smooth_convs.3.conv | 0.147M | 0.151G |
| det_head | 0.329M | 10.909G |
| det_head.binarize | 0.164M | 10.909G |
| det_head.binarize.0 | 0.147M | 9.664G |
| det_head.binarize.1 | 0.128K | 20.972M |
| det_head.binarize.3 | 16.448K | 1.074G |
| det_head.binarize.4 | 0.128K | 83.886M |
| det_head.binarize.6 | 0.257K | 67.109M |
| det_head.threshold | 0.164M | |
| det_head.threshold.0 | 0.147M | |
| det_head.threshold.1 | 0.128K | |
| det_head.threshold.3 | 16.448K | |
| det_head.threshold.4 | 0.128K | |
| det_head.threshold.6 | 0.257K | |
!!!Please be cautious if you use the results in papers. You may need to check if all ops are supported and verify that the flops computation is correct.
```
If you just want to visualize the original dataset, simply set the mode to "original":
```Bash
python tools/visualizations/browse_dataset.py configs/textdet/dbnet/dbnet_resnet50-dcnv2_fpnc_1200e_icdar2015.py -m original
```
Or, to visualize the entire pipeline:
```Bash
python tools/visualizations/browse_dataset.py configs/textdet/dbnet/dbnet_resnet50-dcnv2_fpnc_1200e_icdar2015.py -m pipeline
```
In addition, users can also visualize the original images and their corresponding labels of the dataset by specifying the path to the dataset config file, for example:
```Bash
python tools/visualizations/browse_dataset.py configs/textrecog/_base_/datasets/icdar2015.py
```
Some datasets might have multiple variants. For example, the test split of `icdar2015` textrecog dataset has two variants, which the [base dataset config](/configs/textrecog/_base_/datasets/icdar2015.py) defines as follows:
```python
icdar2015_textrecog_test = dict(
ann_file='textrecog_test.json',
# ...
)
icdar2015_1811_textrecog_test = dict(
ann_file='textrecog_test_1811.json',
# ...
)
```
In this case, you can specify the variant name to visualize the corresponding dataset:
```Bash
python tools/visualizations/browse_dataset.py configs/textrecog/_base_/datasets/icdar2015.py -p icdar2015_1811_textrecog_test
```
Based on this tool, users can easily verify if the annotation of a custom dataset is correct.
### Hyper-parameter Scheduler Visualization
This tool aims to help the user to check the hyper-parameter scheduler of the optimizer (without training), which support the "learning rate" or "momentum"
#### Introduce the scheduler visualization tool
```bash
python tools/visualizations/vis_scheduler.py \
${CONFIG_FILE} \
[-p, --parameter ${PARAMETER_NAME}] \
[-d, --dataset-size ${DATASET_SIZE}] \
[-n, --ngpus ${NUM_GPUs}] \
[-s, --save-path ${SAVE_PATH}] \
[--title ${TITLE}] \
[--style ${STYLE}] \
[--window-size ${WINDOW_SIZE}] \
[--cfg-options]
```
**Description of all arguments**:
- `config`: The path of a model config file.
- **`-p, --parameter`**: The param to visualize its change curve, choose from "lr" and "momentum". Default to use "lr".
- **`-d, --dataset-size`**: The size of the datasets. If set,`build_dataset` will be skipped and `${DATASET_SIZE}` will be used as the size. Default to use the function `build_dataset`.
- **`-n, --ngpus`**: The number of GPUs used in training, default to be 1.
- **`-s, --save-path`**: The learning rate curve plot save path, default not to save.
- `--title`: Title of figure. If not set, default to be config file name.
- `--style`: Style of plt. If not set, default to be `whitegrid`.
- `--window-size`: The shape of the display window. If not specified, it will be set to `12*7`. If used, it must be in the format `'W*H'`.
- `--cfg-options`: Modifications to the configuration file, refer to [Learn about Configs](../user_guides/config.md).
```{note}
Loading annotations maybe consume much time, you can directly specify the size of the dataset with `-d, dataset-size` to save time.
```
#### How to plot the learning rate curve without training
You can use the following command to plot the step learning rate schedule used in the config `configs/textdet/dbnet/dbnet_resnet50-dcnv2_fpnc_1200e_icdar2015.py`:
```bash
python tools/visualizations/vis_scheduler.py configs/textdet/dbnet/dbnet_resnet50-dcnv2_fpnc_1200e_icdar2015.py -d 100
```
## Analysis Tools
### Offline Evaluation Tool
For saved prediction results, we provide an offline evaluation script `tools/analysis_tools/offline_eval.py`. The following example demonstrates how to use this tool to evaluate the output of the "PSENet" model offline.
```Bash
# When running the test script for the first time, you can save the output of the model by specifying the --save-preds parameter
python tools/test.py ${CONFIG_FILE} ${CHECKPOINT_FILE} --save-preds
# Example: Testing on PSENet
python tools/test.py configs/textdet/psenet/psenet_r50_fpnf_600e_icdar2015.py epoch_600.pth --save-preds
# Then, using the saved outputs for offline evaluation
python tools/analysis_tool/offline_eval.py ${CONFIG_FILE} ${PRED_FILE}
# Example: Offline evaluation of saved PSENet results
python tools/analysis_tools/offline_eval.py configs/textdet/psenet/psenet_r50_fpnf_600e_icdar2015.py work_dirs/psenet_r50_fpnf_600e_icdar2015/epoch_600.pth_predictions.pkl
```
`-save-preds` saves the output to `work_dir/CONFIG_NAME/MODEL_NAME_predictions.pkl` by default
In addition, based on this tool, users can also convert predictions obtained from other libraries into MMOCR-supported formats, then use MMOCR's built-in metrics to evaluate them.
| ARGS | Type | Description |
| ------------- | ----- | ----------------------------------------------------------------- |
| config | str | (required) Path to the config. |
| pkl_results | str | (required) The saved predictions. |
| --cfg-options | float | Override configs.[Example](./config.md#command-line-modification) |
### Calculate FLOPs and the Number of Parameters
We provide a method to calculate the FLOPs and the number of parameters, first we install the dependencies using the following command.
```shell
pip install fvcore
```
The usage of the script to calculate FLOPs and the number of parameters is as follows.
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/get_flops.py ${config} --shape ${IMAGE_SHAPE}
```
| ARGS | Type | Description |
| ------- | ---- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| config | str | (required) Path to the config. |
| --shape | int | Image size to use when calculating FLOPs, such as `--shape 320 320`. Default is `640 640` |
For example, you can run the following command to get FLOPs and the number of parameters of `dbnet_resnet18_fpnc_100k_synthtext.py`:
```shell
python tools/analysis_tools/get_flops.py configs/textdet/dbnet/dbnet_resnet18_fpnc_100k_synthtext.py --shape 1024 1024
```
The output is as follows:
```shell
input shape is (1, 3, 1024, 1024)
| module | #parameters or shape | #flops |
| :------------------------ | :------------------- | :------ |
| model | 12.341M | 63.955G |
| backbone | 11.177M | 38.159G |
| backbone.conv1 | 9.408K | 2.466G |
| backbone.conv1.weight | (64, 3, 7, 7) | |
| backbone.bn1 | 0.128K | 83.886M |
| backbone.bn1.weight | (64,) | |
| backbone.bn1.bias | (64,) | |
| backbone.layer1 | 0.148M | 9.748G |
| backbone.layer1.0 | 73.984K | 4.874G |
| backbone.layer1.1 | 73.984K | 4.874G |
| backbone.layer2 | 0.526M | 8.642G |
| backbone.layer2.0 | 0.23M | 3.79G |
| backbone.layer2.1 | 0.295M | 4.853G |
| backbone.layer3 | 2.1M | 8.616G |
| backbone.layer3.0 | 0.919M | 3.774G |
| backbone.layer3.1 | 1.181M | 4.842G |
| backbone.layer4 | 8.394M | 8.603G |
| backbone.layer4.0 | 3.673M | 3.766G |
| backbone.layer4.1 | 4.721M | 4.837G |
| neck | 0.836M | 14.887G |
| neck.lateral_convs | 0.246M | 2.013G |
| neck.lateral_convs.0.conv | 16.384K | 1.074G |
| neck.lateral_convs.1.conv | 32.768K | 0.537G |
| neck.lateral_convs.2.conv | 65.536K | 0.268G |
| neck.lateral_convs.3.conv | 0.131M | 0.134G |
| neck.smooth_convs | 0.59M | 12.835G |
| neck.smooth_convs.0.conv | 0.147M | 9.664G |
| neck.smooth_convs.1.conv | 0.147M | 2.416G |
| neck.smooth_convs.2.conv | 0.147M | 0.604G |
| neck.smooth_convs.3.conv | 0.147M | 0.151G |
| det_head | 0.329M | 10.909G |
| det_head.binarize | 0.164M | 10.909G |
| det_head.binarize.0 | 0.147M | 9.664G |
| det_head.binarize.1 | 0.128K | 20.972M |
| det_head.binarize.3 | 16.448K | 1.074G |
| det_head.binarize.4 | 0.128K | 83.886M |
| det_head.binarize.6 | 0.257K | 67.109M |
| det_head.threshold | 0.164M | |
| det_head.threshold.0 | 0.147M | |
| det_head.threshold.1 | 0.128K | |
| det_head.threshold.3 | 16.448K | |
| det_head.threshold.4 | 0.128K | |
| det_head.threshold.6 | 0.257K | |
!!!Please be cautious if you use the results in papers. You may need to check if all ops are supported and verify that the flops computation is correct.
```