# Data Transforms and Pipeline
In the design of MMOCR, dataset construction and preparation are decoupled. That is, dataset construction classes such as [`OCRDataset`](mmocr.datasets.ocr_dataset.OCRDataset) are responsible for loading and parsing annotation files; while data transforms further apply data preprocessing, augmentation, formatting, and other related functions. Currently, there are five types of data transforms implemented in MMOCR, as shown in the following table.
| | | |
| -------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| Transforms Type | File | Description |
| Data Loading | loading.py | Implemented the data loading functions. |
| Data Formatting | formatting.py | Formatting the data required by different tasks. |
| Cross Project Data Adapter | adapters.py | Converting the data format between other OpenMMLab projects and MMOCR. |
| Data Augmentation Functions | ocr_transforms.py
textdet_transforms.py
textrecog_transforms.py | Various built-in data augmentation methods designed for different tasks. |
| Wrappers of Third Party Packages | wrappers.py | Wrapping the transforms implemented in popular third party packages such as [ImgAug](https://github.com/aleju/imgaug), and adapting them to MMOCR format. |
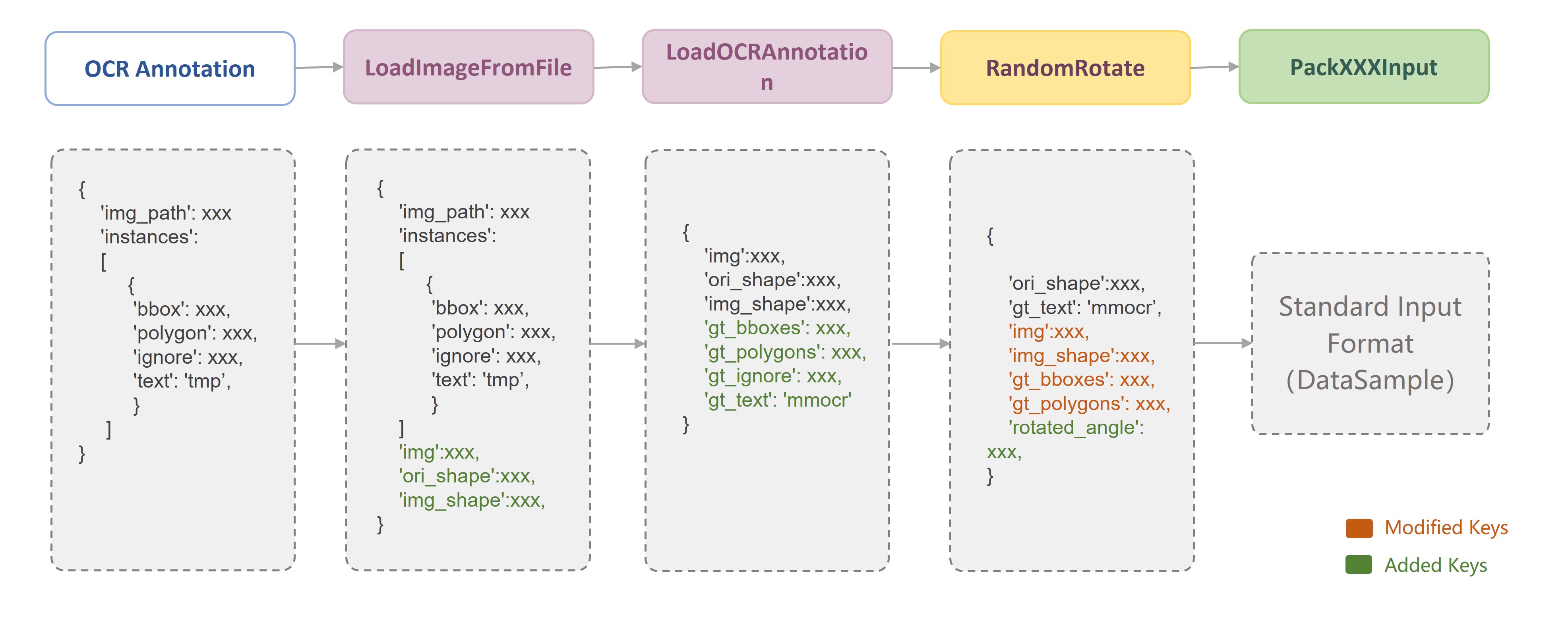
Since each data transform class is independent of each other, we can easily combine any data transforms to build a data pipeline after we have defined the data fields. As shown in the following figure, in MMOCR, a typical training data pipeline consists of three stages: **data loading**, **data augmentation**, and **data formatting**. Users only need to define the data pipeline list in the configuration file and specify the specific data transform class and its parameters:
```python
train_pipeline_r18 = [
# Loading images
dict(
type='LoadImageFromFile',
color_type='color_ignore_orientation'),
# Loading annotations
dict(
type='LoadOCRAnnotations',
with_polygon=True,
with_bbox=True,
with_label=True,
),
# Data augmentation
dict(
type='ImgAugWrapper',
args=[['Fliplr', 0.5],
dict(cls='Affine', rotate=[-10, 10]), ['Resize', [0.5, 3.0]]]),
dict(type='RandomCrop', min_side_ratio=0.1),
dict(type='Resize', scale=(640, 640), keep_ratio=True),
dict(type='Pad', size=(640, 640)),
# Data formatting
dict(
type='PackTextDetInputs',
meta_keys=('img_path', 'ori_shape', 'img_shape'))
]
```
```{tip}
More tutorials about data pipeline configuration can be found in the [Config Doc](../user_guides/config.md#data-pipeline-configuration). Next, we will briefly introduce the data transforms supported in MMOCR according to their categories.
```
For each data transform, MMOCR provides a detailed docstring. For example, in the header of each data transform class, we annotate `Required Keys`, `Modified Keys` and `Added Keys`. The `Required Keys` represent the mandatory fields that should be included in the input required by the data transform, while the `Modified Keys` and `Added Keys` indicate that the transform may modify or add the fields into the original data. For example, `LoadImageFromFile` implements the image loading function, whose `Required Keys` is the image path `img_path`, and the `Modified Keys` includes the loaded image `img`, the current size of the image `img_shape`, the original size of the image `ori_shape`, and other image attributes.
```python
@TRANSFORMS.register_module()
class LoadImageFromFile(MMCV_LoadImageFromFile):
# We provide detailed docstring for each data transform.
"""Load an image from file.
Required Keys:
- img_path
Modified Keys:
- img
- img_shape
- ori_shape
"""
```
```{note}
In the data pipeline of MMOCR, the image and label information are saved in a dictionary. By using the unified fields, the data can be freely transferred between different data transforms. Therefore, it is very important to understand the conventional fields used in MMOCR.
```
For your convenience, the following table lists the conventional keys used in MMOCR data transforms.
| | | |
| ---------------- | --------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| Key | Type | Description |
| img | `np.array(dtype=np.uint8)` | Image array, shape of `(h, w, c)`. |
| img_shape | `tuple(int, int)` | Current image size `(h, w)`. |
| ori_shape | `tuple(int, int)` | Original image size `(h, w)`. |
| scale | `tuple(int, int)` | Stores the target image size `(h, w)` specified by the user in the `Resize` data transform series. Note: This value may not correspond to the actual image size after the transformation. |
| scale_factor | `tuple(float, float)` | Stores the target image scale factor `(w_scale, h_scale)` specified by the user in the `Resize` data transform series. Note: This value may not correspond to the actual image size after the transformation. |
| keep_ratio | `bool` | Boolean flag determines whether to keep the aspect ratio while scaling images. |
| flip | `bool` | Boolean flags to indicate whether the image has been flipped. |
| flip_direction | `str` | Flipping direction, options are `horizontal`, `vertical`, `diagonal`. |
| gt_bboxes | `np.array(dtype=np.float32)` | Ground-truth bounding boxes. |
| gt_polygons | `list[np.array(dtype=np.float32)` | Ground-truth polygons. |
| gt_bboxes_labels | `np.array(dtype=np.int64)` | Category label of bounding boxes. By default, MMOCR uses `0` to represent "text" instances. |
| gt_texts | `list[str]` | Ground-truth text content of the instance. |
| gt_ignored | `np.array(dtype=np.bool_)` | Boolean flag indicating whether ignoring the instance (used in text detection). |
## Data Loading
Data loading transforms mainly implement the functions of loading data from different formats and backends. Currently, the following data loading transforms are implemented in MMOCR:
| | | | |
| ------------------ | --------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------- |
| Transforms Name | Required Keys | Modified/Added Keys | Description |
| LoadImageFromFile | `img_path` | `img`
`img_shape`
`ori_shape` | Load image from the specified path,supporting different file storage backends (e.g. `disk`, `http`, `petrel`) and decoding backends (e.g. `cv2`, `turbojpeg`, `pillow`, `tifffile`). |
| LoadOCRAnnotations | `bbox`
`bbox_label`
`polygon`
`ignore`
`text` | `gt_bboxes`
`gt_bboxes_labels`
`gt_polygons`
`gt_ignored`
`gt_texts` | Parse the annotation required by OCR task. |
| LoadKIEAnnotations | `bboxes` `bbox_labels` `edge_labels`
`texts` | `gt_bboxes`
`gt_bboxes_labels`
`gt_edge_labels`
`gt_texts`
`ori_shape` | Parse the annotation required by KIE task. |
## Data Augmentation
Data augmentation is an indispensable process in text detection and recognition tasks. Currently, MMOCR has implemented dozens of data augmentation modules commonly used in OCR fields, which are classified into [ocr_transforms.py](/mmocr/datasets/transforms/ocr_transforms.py), [textdet_transforms.py](/mmocr/datasets/transforms/textdet_transforms.py), and [textrecog_transforms.py](/mmocr/datasets/transforms/textrecog_transforms.py).
Specifically, `ocr_transforms.py` implements generic OCR data augmentation modules such as `RandomCrop` and `RandomRotate`:
| | | | |
| --------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------- |
| Transforms Name | Required Keys | Modified/Added Keys | Description |
| RandomCrop | `img`
`gt_bboxes`
`gt_bboxes_labels`
`gt_polygons`
`gt_ignored`
`gt_texts` (optional) | `img`
`img_shape`
`gt_bboxes`
`gt_bboxes_labels`
`gt_polygons`
`gt_ignored`
`gt_texts` (optional) | Randomly crop the image and make sure the cropped image contains at least one text instance. The optional parameter is `min_side_ratio`, which controls the ratio of the short side of the cropped image to the original image, the default value is `0.4`. |
| RandomRotate | `img`
`img_shape`
`gt_bboxes` (optional)
`gt_polygons` (optional) | `img`
`img_shape`
`gt_bboxes` (optional)
`gt_polygons` (optional)
`rotated_angle` | Randomly rotate the image and optionally fill the blank areas of the rotated image. |
| | | | |
`textdet_transforms.py` implements text detection related data augmentation modules:
| | | | |
| ----------------- | ------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| Transforms Name | Required Keys | Modified/Added Keys | Description |
| RandomFlip | `img`
`gt_bboxes`
`gt_polygons` | `img`
`gt_bboxes`
`gt_polygons`
`flip`
`flip_direction` | Random flip, support `horizontal`, `vertical` and `diagonal` modes. Defaults to `horizontal`. |
| FixInvalidPolygon | `gt_polygons`
`gt_ignored` | `gt_polygons`
`gt_ignored` | Automatically fixing the invalid polygons included in the annotations. |
`textrecog_transforms.py` implements text recognition related data augmentation modules:
| | | | |
| --------------- | ------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| Transforms Name | Required Keys | Modified/Added Keys | Description |
| RescaleToHeight | `img` | `img`
`img_shape`
`scale`
`scale_factor`
`keep_ratio` | Scales the image to the specified height while keeping the aspect ratio. When `min_width` and `max_width` are specified, the aspect ratio may be changed. |
| | | | |
```{warning}
The above table only briefly introduces some selected data augmentation methods, for more information please refer to the [API documentation](../api.rst) or the code docstrings.
```
## Data Formatting
Data formatting transforms are responsible for packaging images, ground truth labels, and other information into a dictionary. Different tasks usually rely on different formatting transforms. For example:
| | | | |
| ------------------- | ------------- | ------------------- | --------------------------------------------- |
| Transforms Name | Required Keys | Modified/Added Keys | Description |
| PackTextDetInputs | - | - | Pack the inputs required by text detection. |
| PackTextRecogInputs | - | - | Pack the inputs required by text recognition. |
| PackKIEInputs | - | - | Pack the inputs required by KIE. |
## Cross Project Data Adapters
The cross-project data adapters bridge the data formats between MMOCR and other OpenMMLab libraries such as [MMDetection](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection), making it possible to call models implemented in other OpenMMLab projects. Currently, MMOCR has implemented [`MMDet2MMOCR`](mmocr.datasets.transforms.MMDet2MMOCR) and [`MMOCR2MMDet`](mmocr.datasets.transforms.MMOCR2MMDet), allowing data to be converted between MMDetection and MMOCR formats; with these adapters, users can easily train any detectors supported by MMDetection in MMOCR. For example, we provide a [tutorial](#todo) to show how to train Mask R-CNN as a text detector in MMOCR.
| | | | |
| --------------- | -------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------- | ------------------------------------------ |
| Transforms Name | Required Keys | Modified/Added Keys | Description |
| MMDet2MMOCR | `gt_masks` `gt_ignore_flags` | `gt_polygons`
`gt_ignored` | Convert the fields used in MMDet to MMOCR. |
| MMOCR2MMDet | `img_shape`
`gt_polygons`
`gt_ignored` | `gt_masks` `gt_ignore_flags` | Convert the fields used in MMOCR to MMDet. |
## Wrappers
To facilitate the use of popular third-party CV libraries in MMOCR, we provide wrappers in `wrappers.py` to unify the data format between MMOCR and other third-party libraries. Users can directly configure the data transforms provided by these libraries in the configuration file of MMOCR. The supported wrappers are as follows:
| | | | |
| ------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------- |
| Transforms Name | Required Keys | Modified/Added Keys | Description |
| ImgAugWrapper | `img`
`gt_polygons` (optional for text recognition)
`gt_bboxes` (optional for text recognition)
`gt_bboxes_labels` (optional for text recognition)
`gt_ignored` (optional for text recognition)
`gt_texts` (optional) | `img`
`gt_polygons` (optional for text recognition)
`gt_bboxes` (optional for text recognition)
`gt_bboxes_labels` (optional for text recognition)
`gt_ignored` (optional for text recognition)
`img_shape` (optional)
`gt_texts` (optional) | [ImgAug](https://github.com/aleju/imgaug) wrapper, which bridges the data format and configuration between ImgAug and MMOCR, allowing users to config the data augmentation methods supported by ImgAug in MMOCR. |
| TorchVisionWrapper | `img` | `img`
`img_shape` | [TorchVision](https://github.com/pytorch/vision) wrapper, which bridges the data format and configuration between TorchVision and MMOCR, allowing users to config the data transforms supported by `torchvision.transforms` in MMOCR. |
### `ImgAugWrapper` Example
For example, in the original ImgAug, we can define a `Sequential` type data augmentation pipeline as follows to perform random flipping, random rotation and random scaling on the image:
```python
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
aug = iaa.Sequential(
iaa.Fliplr(0.5), # horizontally flip 50% of all images
iaa.Affine(rotate=(-10, 10)), # rotate by -10 to +10 degrees
iaa.Resize((0.5, 3.0)) # scale images to 50-300% of their size
)
```
In MMOCR, we can directly configure the above data augmentation pipeline in `train_pipeline` as follows:
```python
dict(
type='ImgAugWrapper',
args=[
['Fliplr', 0.5],
dict(cls='Affine', rotate=[-10, 10]),
['Resize', [0.5, 3.0]],
]
)
```
Specifically, the `args` parameter accepts a list, and each element in the list can be a list or a dictionary. If it is a list, the first element of the list is the class name in `imgaug.augmenters`, and the following elements are the initialization parameters of the class; if it is a dictionary, the `cls` key corresponds to the class name in `imgaug.augmenters`, and the other key-value pairs correspond to the initialization parameters of the class.
### `TorchVisionWrapper` Example
For example, in the original TorchVision, we can define a `Compose` type data transformation pipeline as follows to perform color jittering on the image:
```python
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
aug = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ColorJitter(
brightness=32.0 / 255, # brightness jittering range
saturation=0.5) # saturation jittering range
])
```
In MMOCR, we can directly configure the above data transformation pipeline in `train_pipeline` as follows:
```python
dict(
type='TorchVisionWrapper',
op='ColorJitter',
brightness=32.0 / 255,
saturation=0.5
)
```
Specifically, the `op` parameter is the class name in `torchvision.transforms`, and the following parameters correspond to the initialization parameters of the class.